Hello, from The Literacy Bug,
At this time, we’d like to take the opportunity to share some links to a few quality (mostly free) educational resources that we have come across in the last few years.
We appreciate that many of you may be home schooling children during the present COVID-19 outbreak, or you may be organising remote teaching/support for children. The following may serve as useful resources.
We’d also like to ask the community to share their own suggestions. If you have further recommended resources, please add a comment to the blog or send us an email at info@theliteracybug.com. We’d love to hear from you.
Please note: The following suggestions are not designed to replace the teaching ideas that dedicated teachers are sending home for parents. It’s important to work together to avoid a significant disruption to children’s education.
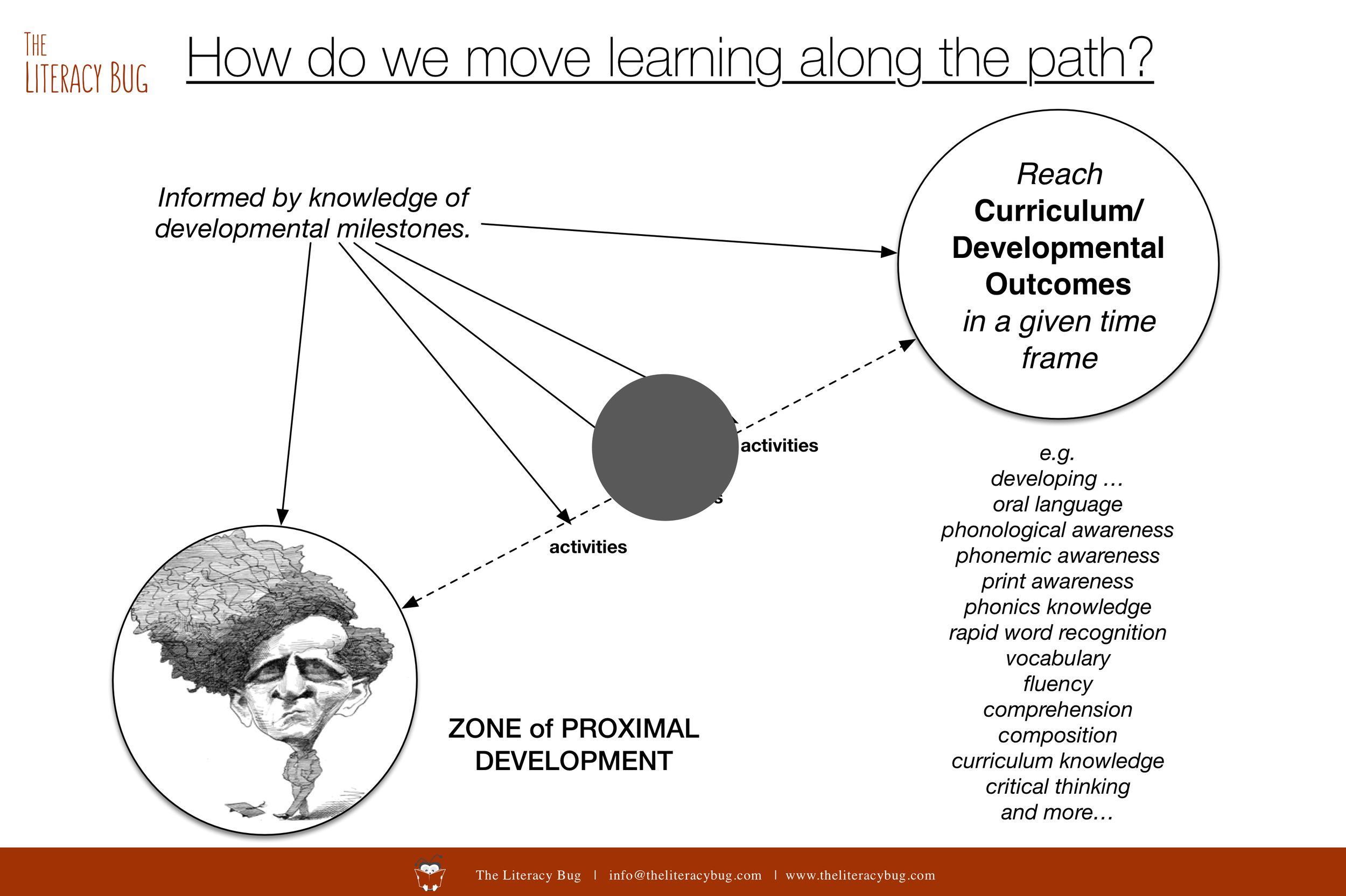
If you are looking for suggestions consistent with the “Big Six”, then look here …
Research clearly demonstrates that budding readers benefit from activities that develop the “Big Six” skills: oral language, phonological awareness, phonics, vocabulary, fluency and comprehension.
This is where the FLORIDA CENTRE FOR READING RESEARCH (FCRR) can help. Their comprehensive set of Student Centre Activities provides a wealth of teaching ideas across the Big Six skills for a wide range of ages (preschool to Grade 5). All materials are available freely to the public.
Preschool activities: https://fcrr.org/resources/resources_vpk.html
Kindie to Grade 5 activities: https://fcrr.org/resources/resources_sca.html
We do note that it can be a bit daunting to teach using just the activities above, which is why FCRR also includes further planning, teaching and monitoring resources:
Suggested Instructional Routines: http://www.fcrr.org/assessment/ET/routines/routines.html
Scaffolds for Planning Instruction and Tracking Progress: http://www.fcrr.org/assessment/ET/guides/guides.html
We all know how to read to our preschoolers … right? … here are a few extra ideas to support children’s early literacy skills
Developed by the Crane Centre for Early Childhood Research and Policy at Ohio State University, READ IT AGAIN-PREK! is a practitioner-friendly, scientifically based, and relevant curricular supplement designed to develop and strengthen young children’s early foundations in language and literacy.
All lessons are organized around adult-child readings of high-quality storybooks.
Each lesson idea is designed to systematically build children’s language and literacy abilities in four areas key pre-literacy areas:
Vocabulary
Narrative
Phonological awareness
Print knowledge
Please note that each lesson is centred around particular picture books. In many cases, you will not have access to these exact books, but you can explore the teaching ideas in the support material and apply these ideas to the book you have access to.
There are a lot of phonics apps out there, so we have a couple recommendations that may spark your interest
FEED THE MONSTER is a free, engaging Android game that helps children develop basic understanding of vowel sounds, consonant sounds and simple words. In other words, children:
Learn letter names;
Learn letter sounds;
Learn to sound out simple words; and
Practice reading in an interactive setting at varying levels of difficulty
What’s more important is that Feed the Monster is available in over 40 languages including English, Español, Français, Kiswahili, Hindi, and Farsi. The game was initially developed with support from the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation and USAID and was a winner in the EduApp4Syria contest. It is being further developed by Curious Learning, a global nonprofit focused on promoting literacy.
The various Feed the Monster games (including English) can be found on GooglePlay at https://play.google.com/store/apps/developer?id=Curious%20Learning
SOUNDS ENGLISH PHONICS is an innovative new learn-to-read app from the educational company Zaprendo.
It is important to note that the game is NOT a beginning phonics app. It is designed for students who have reached the 'early reading phase’ (a reading age of about 6.5 years) and is based on 92 written sounds that occur most frequently in early reading material. Many of these are vowel dipthongs as well as blended consonant sounds - such as 'bl'. This makes good sense for early readers (as opposed to emergent readers) as this extends students who have already mastered basic short vowels and CVC constructs.
The app recommends that learners focus on three sounds per day (with accompanying words). All learning is organised around the “Great Learning Tree”, which provides a visible indications of the learner’s progress.
What is most impressive is the adaptive learning feature, which monitors the words that children get right and wrong. The system uses this information to determine and modify the sequence of letter-sounds that learners encounter in the game.
Please explore and enjoy! And note, this is a paid app.
Are you looking for free reading materials for early readers in English but also in a range of other languages?
STORYWEAVER is a digital repository of multilingual stories for children from Pratham Books. Storyweaver is designed to provide children with richly illustrated, open-licensed children's stories in mother tongue languages (including English). The stories are levelled by reading difficulty, so you can find free texts at the right level for your emerging reader.
All the stories are available online and offline. They are downloadable as PDFs for easy printing, and there are also a number of readalong stories in the repository.
Another resource with a similar intent is the GLOBAL DIGITAL LIBRARY from the Global Book Alliance. Keep a look out for the following resource as it is sure to grow in the coming months.
Are you looking for accessible, information texts for developing readers?
TEXTPROJECT’S “FYI FOR KIDS” resource provides a wealth of free, short, accessible texts with accompanying activities. These texts can be used to help developing readers focus increasing attention on how to extract key information as they read.
There are texts in a range of difficulties and in diverse subject areas, including science, social studies, arts, music, history and culture. The website also now includes an easy-to-use search tool to filter text by difficulty and topic.
Are you looking for even more reading materials to help expand learners’ understanding of the world around them?
NEWSELA is an innovative site with resources designed to build reading comprehension from a relevant, contemporary source of nonfiction: the daily news.
Newsela includes articles ranging from sport, the arts, to politics, and more. All articles are sourced from reputable new outlets like the Washington Post, Scientific American, the History Channel, and much, much more.
The key is this, though: Newsela creates multiple versions of each article for different skills and abilities. In other words, there will be version written at a Grade 3 level, a Grade 5 level, a Grade 7 level, and so on.
It makes it easy for an entire class to read the same content yet differentiated to suit differing levels of reading skills. In other words, academically challenging content can be presented within the zone of proximal development of the learner.
Please explore and enjoy. You’ll be pleased that you did.
Are you wishing to challenge learners with academic vocabulary and enagaging topics?
WORD GENERATION is a research-based program for late primary and middle school students which is designed to teach academic vocabulary in language arts, math, science and social studies classes. It is a program that builds academic vocabulary across subject areas by facilitating deep discussion about concepts and issues of concern to children and young people.
Each unit introduces approximately five or six high-utility academic “focus words” and is designed to offer a variety of texts, word-learning activities, writing tasks, and debate and/or discussion opportunities. Specifically, each unit helps:
expand general and content-oriented academic vocabulary;
build the reasoning and argumentation skills that are necessary for learning in all content areas; and
build reading comprehension and content-area literacy by providing students with motivating text, opportunities for discussion and debate, and weekly writing.
Please explore and enjoy:
Elementary School Years: https://www.serpinstitute.org/wordgen-elementary
Middle School Years: https://www.serpinstitute.org/wordgen-weekly
Do you need resources to help adolescent readers develop key fluency and deep comprehension skills?
Serp Institute’s STARI program (or Strategic Adolescent Reading Intervention) is a literature-focused intervention for students in grades 6-9 who read two or more years below grade level. STARI addresses gaps in fluency, decoding, reading stamina, and comprehension, aiming to move struggling students to higher levels of proficiency whilst providing cognitively challenging content that is aligned to the Common Core and other 21st century standards.
Each units includes a range of materials to support growing fluency, comprehension, critical thinking and academic development.
Check this one out: https://www.serpinstitute.org/stari
COMMONLIT is a nonprofit education technology organization dedicated to ensuring that all students develop strong reading, writing, communication, and problem-solving skills.
The system includes over 2,000 high-quality free reading passages for grades 3-12, complemented by questions, paired readings and activities to promote deep consideration of important social, environmental and historical issues.
This includes:
individual texts (organised by grade level and theme);
texts organised into units of study; and
novel (book) studies that guide students into deep, critical thinking.
Please note that CommonLit now includes a range of Spanish content, as well.
Last but not least, the COMPREHENSION CIRCUIT TRAINING (CCT) resource from The Meadows Centre provides a range of scaffolds to support youth to read with an analytical and critical mind. The CCT resource is part of the broader PACT project (Promoting Adolescents’ Comprehension of Text)
Please stay connected and reach out if you have further ideas and resources that you’d like to share
We are really pleased to share this list with you. It’s not a comprehensive list, but hopefully it has some useful ideas. To explore further, please visit our list of recommended links.
If you’d like to add any further recommendations, please let us know. We are keen to hear from you. Please add a comment to the blog or send us an email at info@theliteracybug.com.
Bye for now.